# 工具函数
# Array Flatten
- 写一个JS函数,实现数组扁平化,只减少一级嵌套
- 如输入
[1,[2,[3],4],输出[1,2,[3],4]
# 思路
TIP
定义空数组arr=们。遍历当前数组 如果item非数组,则累加到arr 如果item是数组,则遍历之后累加到arr
/**
* 数组扁平化,使用 push
* @param arr arr
*/
export function flatten1(arr: any[]): any[] {
const res: any[] = []
arr.forEach(item => {
if (Array.isArray(item)) {
item.forEach(n => res.push(n))
} else {
res.push(item)
}
})
return res
}
/**
* 数组扁平化,使用 concat
* @param arr arr
*/
export function flatten2(arr: any[]): any[] {
let res: any[] = []
arr.forEach(item => {
res = res.concat(item)
})
return res
}
// // 功能测试
// const arr = [1, [2, [3], 4], 5]
// console.info( flatten2(arr) )
# Array Flatten 彻底拍平
写一个S函数,实现数组扁平化,减少所有嵌套的层级 如输入
[1,[2,[3],4],输出[1,2,,3,4]
/**
* 数组深度扁平化,使用 push
* @param arr arr
*/
export function flattenDeep1(arr: any[]): any[] {
const res: any[] = []
arr.forEach(item => {
if (Array.isArray(item)) {
const flatItem = flattenDeep1(item) // 递归
flatItem.forEach(n => res.push(n))
} else {
res.push(item)
}
})
return res
}
/**
* 数组深度扁平化,使用 concat
* @param arr arr
*/
export function flattenDeep2(arr: any[]): any[] {
let res: any[] = []
arr.forEach(item => {
if (Array.isArray(item)) {
const flatItem = flattenDeep2(item) // 递归
res = res.concat(flatItem)
} else {
res = res.concat(item)
}
})
return res
}
# getType函数-获取类型
/**
* 获取详细的数据类型
* @param x x
*/
export function getType(x: any): string {
const originType = Object.prototype.toString.call(x) // '[object String]'
const spaceIndex = originType.indexOf(' ')
const type = originType.slice(spaceIndex + 1, -1) // 'String'
return type.toLowerCase() // 'string'
}
// // 功能测试
// console.info( getType(null) ) // 'null'
// console.info( getType(undefined) )
// console.info( getType(100) )
// console.info( getType('abc') )
// console.info( getType(true) )
// console.info( getType(Symbol()) )
// console.info( getType({}) )
// console.info( getType([]) )
// console.info( getType(() => {}) )
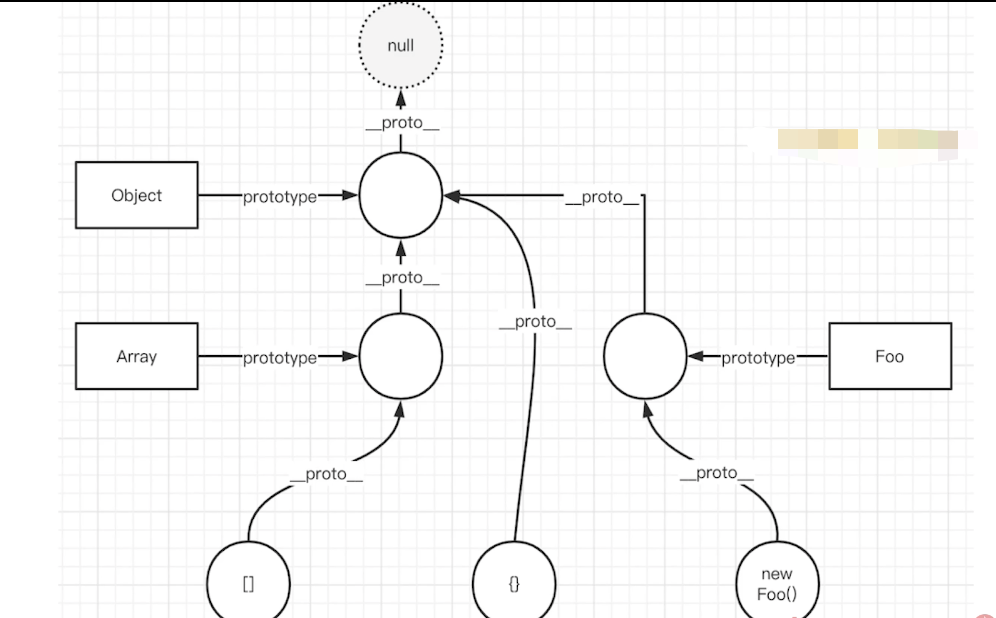
# new 一个对象发生了什么?请手写代码表示
class 是function的语法糖
TIP
- 创建一个空对象oj,继承构造函数的原型
- 执行构造函数(将obj作为this)
- 返回obj
class Foo {
name:string;
city:string;
constructor(name){
this.name = name;
this.city = 'bj'
}
getName(){
return this.name
}
}
const f = new Foo('ljh')
f.getName()
new
export function customNew<T>(constructor: Function, ...args: any[]): T {
// 1. 创建一个空对象,继承 constructor 的原型
const obj = Object.create(constructor.prototype);
// 2. 将 obj 作为 this ,执行 constructor ,传入参数
constructor.apply(obj, args);
// 3. 返回 obj
return obj;
}
# {}和Object.prototype 区别
TIP
- {}创建空对象,原型指向Object.prototype
- Object.create创建空对象,原型指向传入的参数
# 遍历dom树
# 广度优先
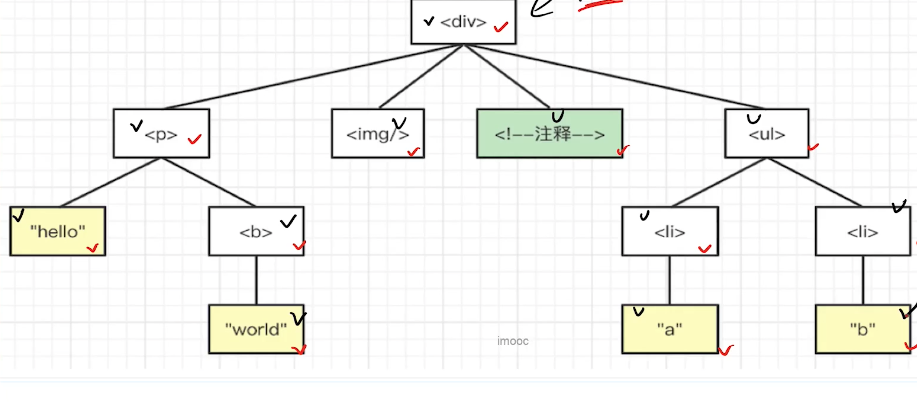
# 深度优先
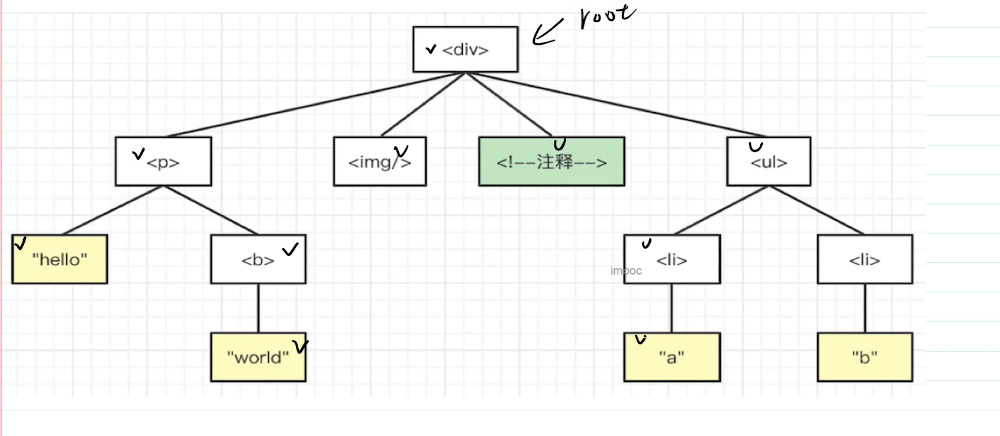
# 手写一个curry函数,把其他函数柯里化
export function curry(fn: Function) {
const fnArgsLength = fn.length // 传入函数的参数长度
let args: any[] = []
// ts 中,独立的函数,this 需要声明类型
function calc(this: any, ...newArgs: any[]) {
// 积累参数
args = [
...args,
...newArgs
]
if (args.length < fnArgsLength) {
// 参数不够,返回函数
return calc
} else {
// 参数够了,返回执行结果
return fn.apply(this, args.slice(0, fnArgsLength))
}
}
return calc
}
// function add(a: number, b: number, c: number): number {
// return a + b + c
// }
// // add(10, 20, 30) // 60
// const curryAdd = curry(add)
// const res = curryAdd(10)(20)(30) // 60
// console.info(res)
# instanceof 原理是什么?代码实现
/**
* 自定义 instanceof
* @param instance instance
* @param origin class or function
*/
export function myInstanceof(instance: any, origin: any): boolean {
if (instance == null) return false // null undefined
const type = typeof instance
if (type !== 'object' && type !== 'function') {
// 值类型
return false
}
let tempInstance = instance // 为了防止修改 instance
while (tempInstance) {
if (tempInstance.__proto__ === origin.prototype) {
return true // 配上了
}
// 未匹配
tempInstance = tempInstance.__proto__ // 顺着原型链,往上找
}
return false
}
// // 功能测试
// console.info( myInstanceof({}, Object) )
// console.info( myInstanceof([], Object) )
// console.info( myInstanceof([], Array) )
// console.info( myInstanceof({}, Array) )
// console.info( myInstanceof('abc', String) )
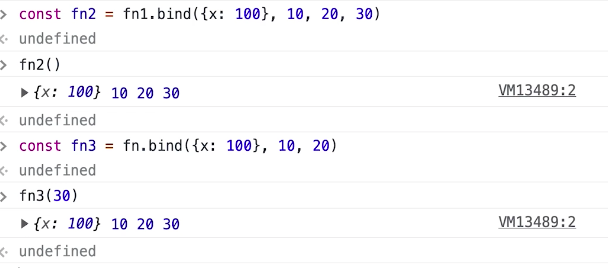
# 手写bind
TIP
- 返回一个新函数,但不执行
- 绑定this和部分参数
- 如是箭头函数,无法改变this,只能改变参数
TIP
分析
- 返回新函数
- 绑定this
- 同时绑定执行时的参数(apply或者call)
// @ts-ignore
Function.prototype.customBind = function (context: any, ...bindArgs: any[]) {
// context 是 bind 传入的 this
// bindArgs 是 bind 传入的各个参数
const self = this // 当前的函数本身
return function (...args: any[]) {
// 拼接参数
const newArgs = bindArgs.concat(args)
return self.apply(context, newArgs)
}
}
// // 功能测试
// function fn(this: any, a: any, b: any, c: any) {
// console.info(this, a, b, c)
// }
// // @ts-ignore
// const fn1 = fn.customBind({x: 100}, 10)
// fn1(20, 30)
# apply和call
TIP
应用
- bind返回一个新函数(不执行),cal和apply会立即执行函数
- 绑定this
- 传入执行参数
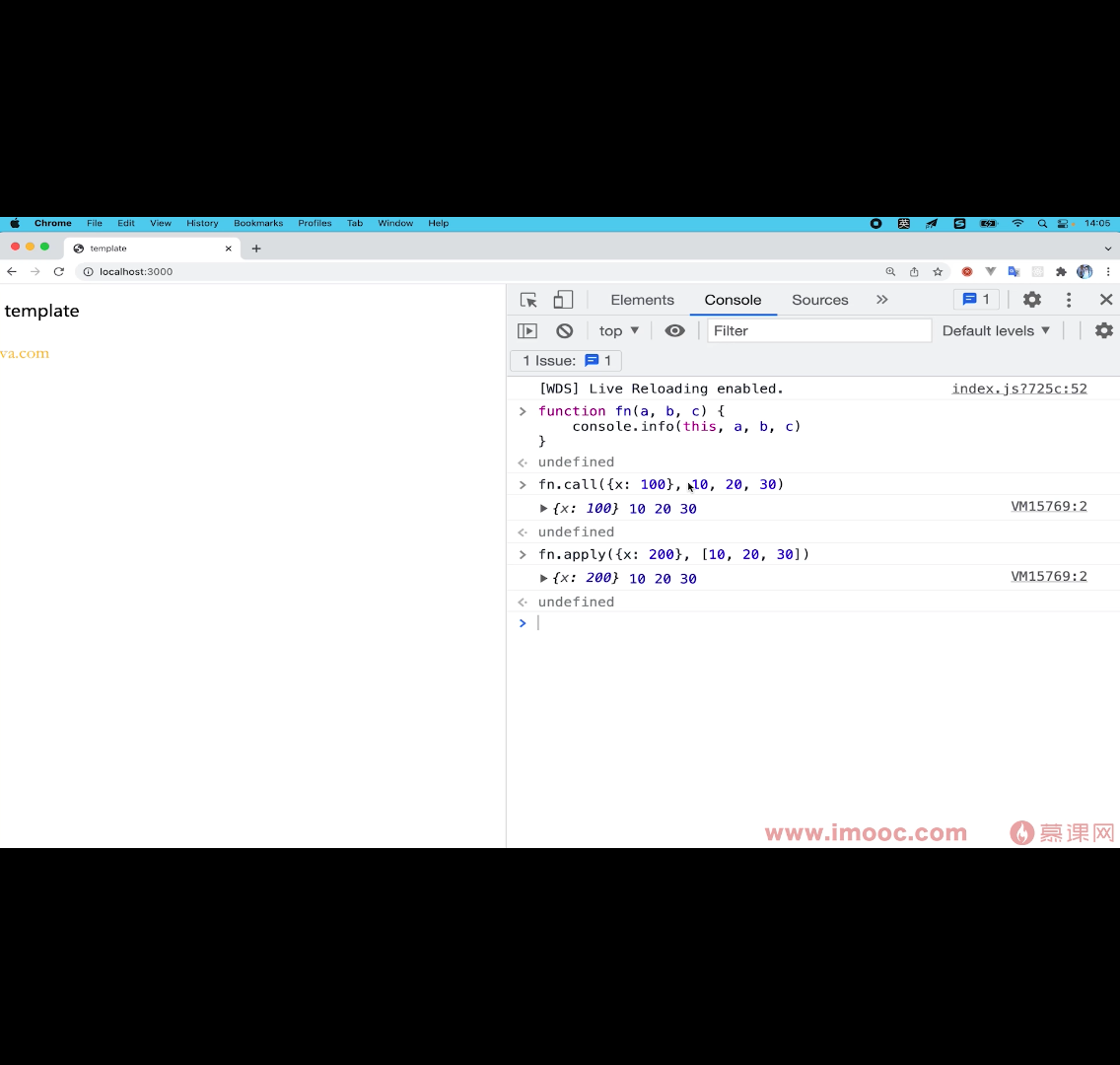
# 如何在函数中绑定this

// @ts-ignore
Function.prototype.customCall = function (context: any, ...args: any[]) {
if (context == null) context = globalThis
if (typeof context !== 'object') context = new Object(context) // 值类型,变为对象
const fnKey = Symbol() // 不会出现属性名称的覆盖
context[fnKey] = this // this 就是当前的函数
const res = context[fnKey](...args) // 绑定了 this
delete context[fnKey] // 清理掉 fn ,防止污染
return res
}
// @ts-ignore
Function.prototype.customApply = function (context: any, args: any[] = []) {
if (context == null) context = globalThis
if (typeof context !== 'object') context = new Object(context) // 值类型,变为对象
const fnKey = Symbol() // 不会出现属性名称的覆盖
context[fnKey] = this // this 就是当前的函数
const res = context[fnKey](...args) // 绑定了 this
delete context[fnKey] // 清理掉 fn ,防止污染
return res
}
function fn(this: any, a: any, b: any, c: any) {
console.info(this, a, b, c)
}
// // @ts-ignore
// fn.customCall({x: 100}, 10, 20, 30)
// @ts-ignore
// fn.customApply({x: 200}, [100, 200, 300])
# 首页EventBus 自定义事件
TIP
- on绑定的事件可以连续执行,除非off
- once绑定的函数emit一次即删除,也可以未执行而被off
export default class EventBus {
/**
* {
* 'key1': [
* { fn: fn1, isOnce: false },
* { fn: fn2, isOnce: false },
* { fn: fn3, isOnce: true },
* ]
* 'key2': [] // 有序
* 'key3': []
* }
*/
private events: {
[key: string]: Array<{fn: Function; isOnce: boolean}>
}
constructor() {
this.events = {}
}
on(type: string, fn: Function, isOnce: boolean = false) {
const events = this.events
if (events[type] == null) {
events[type] = [] // 初始化 key 的 fn 数组
}
events[type].push({ fn, isOnce })
}
once(type: string, fn: Function) {
this.on(type, fn, true)
}
off(type: string, fn?: Function) {
if (!fn) {
// 解绑所有 type 的函数
this.events[type] = []
} else {
// 解绑单个 fn
const fnList = this.events[type]
if (fnList) {
this.events[type] = fnList.filter(item => item.fn !== fn)
}
}
}
emit(type: string, ...args: any[]) {
const fnList = this.events[type]
if (fnList == null) return
// 注意
this.events[type] = fnList.filter(item => {
const { fn, isOnce } = item
fn(...args)
// once 执行一次就要被过滤掉
if (!isOnce) return true
return false
})
}
}
// const e = new EventBus()
// function fn1(a: any, b: any) { console.log('fn1', a, b) }
// function fn2(a: any, b: any) { console.log('fn2', a, b) }
// function fn3(a: any, b: any) { console.log('fn3', a, b) }
// e.on('key1', fn1)
// e.on('key1', fn2)
// e.once('key1', fn3)
// e.on('xxxxxx', fn3)
// e.emit('key1', 10, 20) // 触发 fn1 fn2 fn3
// e.off('key1', fn1)
// e.emit('key1', 100, 200) // 触发 fn2